How a bi-metal thermometer works

A bi-metal thermometer is a temperature measuring device. Using a bimetallic strip, it converts the media temperature into mechanical displacement. Bimetallic strip consists of two different metals with different coefficients of thermal expansion. Bi-metal thermometers are used in residential appliances such as air conditioners, stoves and industrial appliances such as heaters, hot wires, refineries, etc. They are a simple, durable and cost-effective way to measure temperature.
 Construction and design
Construction and design
Bi-metal thermometer works using two basic properties of metal: 1- Thermal expansion property of metal 2- Thermal expansion coefficient of different metals for a different temperature.
The main component of a bi-metal thermometer is a bi-metal strip. Bimetallic strip is composed of two thin strips of different metals, each with different coefficients of thermal expansion. Thermal expansion is the property of a metal to change its shape or volume with a change in temperature. Metal strips are joined together by fusion or riveting. The strips are fixed from one end and move from the other end. The two metals commonly used are steel and copper, but steel and brass can also be used. Because their thermal expansion varies, the lengths of these metals change for the same temperature at different speeds. Due to this property, when the temperature changes, the metal strip expands on one side and does not expand on the other side, which causes a bending effect. This can be seen in Figure 2. As the temperature rises, the bar rotates in the direction of the metal with a lower temperature coefficient. As the temperature decreases, the strip bends in the direction of the metal with a higher temperature coefficient. Shows the deviation of the temperature change bar. This bending motion is connected to the dial plate of the thermometer and thus removes the media temperature. Calibration is an important step in ensuring that the temperature is read correctly.

Figure 2: Bimetallic strip: fixed end (A), free end (B), deflection (C), bi-metal strip (D)
Advantages and disadvantages of Bi-metal thermometers
Advantages of Bi-metal Thermometers
Simple and sturdy design
Less than other thermometers
They are completely mechanical and do not require an energy source to work.
Easy installation and maintenance
Almost linear response to temperature change
Suitable for wide temperature ranges
Disadvantages of Bi-metal Thermometers
They are not recommended to use at very high temperatures.
They may need repeated calibration.
May not have accurate readings for low temperatures.
Types of bi-metal thermometers
There are two bi-metal thermometers, the spiral bar bi-metal thermometer and the spiral bar bi-metal thermometer. Helical and helical strips are used to keep the thermometer size in a controllable range.
Bi-metal spiral bar thermometer:
As the name implies, a spiral bimetallic strip is used to measure the temperature of this type of thermometer. The pointer is connected via a shaft at the free end of the bar. This strip is wound in a spiral inside the stem, as shown in Figure 3. As the temperature increases, the helical bar senses a change in temperature. The strip metal expands with a higher coefficient of thermal expansion and twists along the stem and rotates the shaft. This rotation causes the indicator to dial its position on the screen, which indicates the media temperature. As the temperature decreases, the metal contracts with a lower coefficient of thermal expansion and rotates the shaft. It then reads the low temperature indicator on the screen. These are mostly used for industrial applications because they can be placed inside a thermometer that operates in a high temperature and pressure environment. You can also read the article about temperature transmitter for more information.
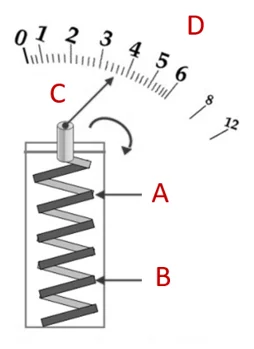
Figure 3: Bi-metal spiral bar thermometer: Bi-metal spiral (A), lamp (B), pointer (C), temperature scale (D)
Bi-metal spiral bar thermometer
To measure the temperature in a bi-metal helical tape thermometer, a helical tape is used, as shown in Figure 4. As the temperature increases, the two metal strips expand differently. This creates a bending effect and the tape becomes coiled so that the metal with a higher thermal coefficient forms the outer side of the arc. As the temperature decreases, the metal with a lower thermal coefficient forms the inner layer of the arc. The indicator and the plate connected to the helix show this deformation, which indicates the temperature of the medium. They are mostly used for thermostats or measuring ambient temperature, because they are sensitive to low temperature changes.
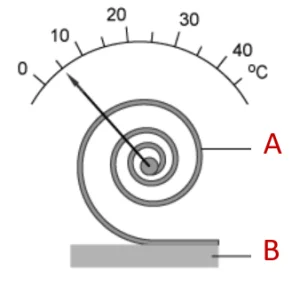
Figure 4: Bi-metal spiral bar thermometer: Bi-metal bar (A), fixed end (B)
Selection criteria
When choosing a Bi-metal thermometer for your application, you should consider the following selection criteria:
Temperature range
Bi-metal thermometer should be at high and low temperature. Due to the extreme temperature, the metals may reach their expansion point and not be destroyed, causing permanent damage to the thermometer.
Stem
Stem length and diameter for a bi-metal stem thermometer should be determined as required by the program. This may require determining the immersion length or depth of the reservoir where the thermometer is used.
Thermol
The thermol is a cylindrical tube that protects the temperature sensors installed in industrial applications. This acts as a barrier to protect expensive thermometers from possible process fluid damage. Thermol should be used in cases where the stem is exposed to temperature, pressure, high velocity or corrosive liquid. By installing a thermometer, thermometers can be easily disassembled and replaced without stopping the process. Because the thermol protects the thermometer, it lasts longer and reduces maintenance and replacement costs.
Thermometer type
Bi-metal thermometers can have a helical strip or a helical strip. Spiral bar thermometers are preferred for industrial applications such as refineries, oil burners, etc. Bimetallic strips are screwed into the stem and can be supported by thermol to operate at extreme temperatures and pressures. Spiral strip thermometers are used in thermostats for sensitivity to low temperature changes.
Calibration of bi-metal thermometer
The most accurate method for calibrating a bimetallic thermometer is the ice point method. To calibrate a bi-metal thermometer using this method, completely fill a glass with ice, add cold water, and leave for 4 to 5 minutes. Then, place the stem of the thermometer in ice water. Make sure the stem does not hit the bottom or side of the glass. Let it move until the dial stops. If the thermometer is accurate, it should be at 0 ° C or 32 ° F. Otherwise, rotate the nut at the bottom of the plate to eat 0 ° C. Check regular intervals to ensure accuracy. Depending on the needs of your application, a weekly or monthly thermometer calibration process should be performed.
Applications
Gas cooler
Thermostat
Control devices
Heater
Furnaces
Hot wires
Refineries
Oil burners
Rose Calibration Company in Melbourne, Australia with over ten years of experience of all calibration, maintenance, and repair services throughout Australia. If you live in Sydney, Melbourne, Adelaide, Perth, Geelong, and Brisbane, you can receive your quote in less than two hours by fill-up the form via the “Booking” link.

