
Supply of equipment for oil, gas and petrochemical industries, importer of George Fisher rotameters
What is a Rotameter ?
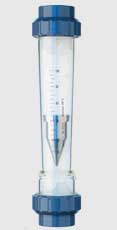
rotameter:
One of the most widely used devices in the industry today is the rotameter. The George Fisher Rotameter is a flowmeter that can measure the flow rate of a fluid (liquid or gas) through a pipe.
Uses of Rotameter:
It is very common to use a rotameter to measure the flow rate of a fluid. rotameters consist of a conical duct (a glass tube whose diameter decreases with a gentle slope) inside which is a floating object about the size of the base of a glass tube. rotameters are installed vertically and current enters it.
Due to the passage of fluid flow from the bottom to the top of the rotameters, a resistive force is applied to this vessel and moves it upwards. As the float rises, the cross-sectional area of the rotameter increases and so does the flow level between the float and the rotameter conical duct.
How the rotameter works:
The float rises to the point where the resistive force of the fluid, the force of Archimedes and the weight of the fluid cancel each other out and the system reaches equilibrium. In this case, the floating location, which is read directly from the rotameter , represents the flow rate. The higher the flow rate through the rotameter, the higher the floating location.
In most rotameter functions, the flow rate is read directly from the ratings written on the glass tube.
In some cases, an automatic sensor measures the height of a floating object. These rotameters are often made of steel or other materials resistant to high pressure fluids.
Rotameters may range in size from 0.25 inches to 6 inches in size and measure a wider range of current than the Oriflate Plate with an accuracy of 2%. Maximum operating pressure when made of glass. psig 300.


